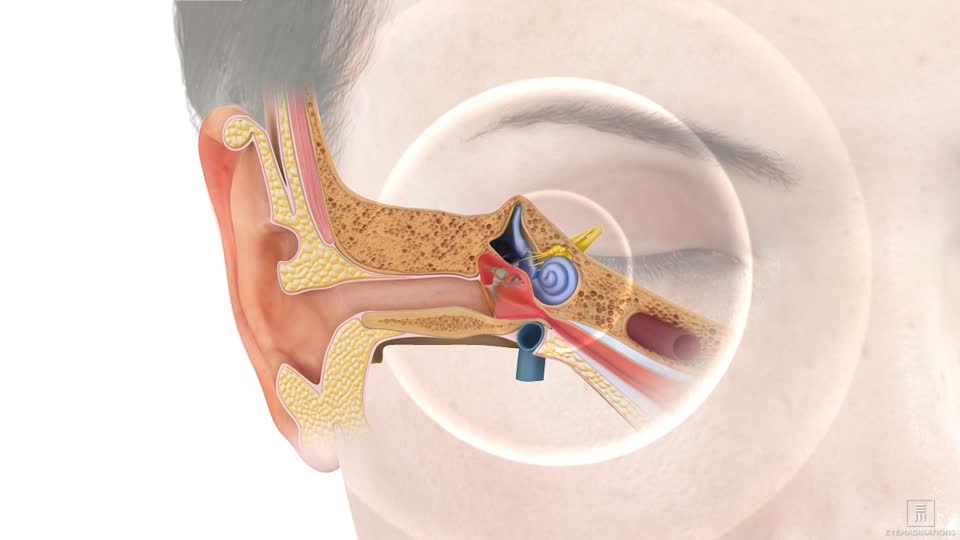
Eustachian tube disorder is defined as blockage of the Eustachian tubes, which result from excessive pressure on the inner ear. As a result of this pressure, the Eustachian tubes can become either inflamed or congested.
The Eustachian tubes are large sinus-like tubes located in the inner ear between the neck and the back of the head
These sinuses are designed to prevent noise, pressure and fluid buildup, and to drain waste products from the ear. Eustachian tubes can become blocked for several reasons, for example:
Inflammation of the Eustachian bone due to fluid buildup can be very painful. This can cause pain and ringing in the ears. People with this condition often have difficulty hearing. They may also experience headaches, ear pain, or ear tenderness.
In people with sinus infections or sinusitis, pressure in the ear may increase, causing symptoms such as fever ear pain, discharge from the ears, and sometimes dizziness. In addition, it can be difficult for people with this condition to close their Eustachian tubes while they sleep.
If the Eustachian tubes are blocked, the person may begin to experience nausea, dizziness, headaches, and vomiting. If left untreated, the condition can cause permanent damage to the inner ear. Once this happens, the person will have a hearing impairment.
Most people with an Eustachian tube do not have serious health problems. However, if left untreated, it can cause hearing loss or permanent damage to the Eustachian tube. When the Eustachian tubes are full, they become less sensitive to sound. This means they won't hear as well as they used to.
Eustachians that become blocked, inflamed, or clogged are usually treated with surgery. The Eustachian tubes can be opened, and the blockages can be removed. This can help relieve the pain caused by these conditions.
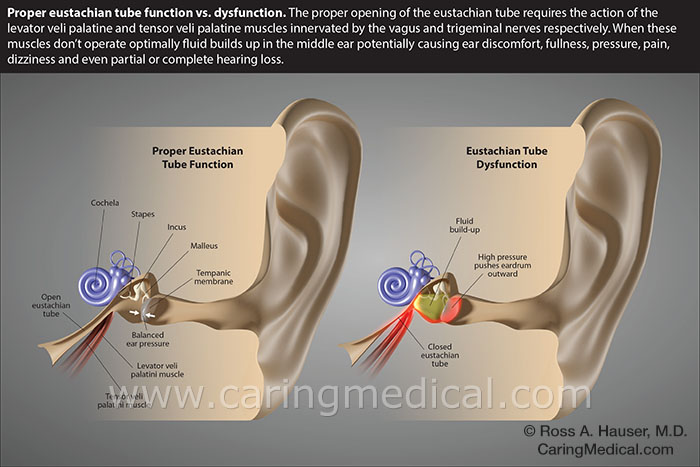
This condition is very common among people who have hearing loss, but this is not the only cause for Eustachial membrane disorder. It is also a leading cause for tinnitus (tiny ears). Therefore, if you have Eustachial obstruction, tinnitus is almost always an underlying problem.
Eustachian blockage, which is usually caused by sinus inflammation, is usually treated with decongestants and antibiotic drops. A doctor might also recommend surgery if the blockage is severe. However, in most cases, Eustachian blockage is a temporary condition and can be treated with antibiotics. Once antibiotics have taken effect, the blockage will stop and Eustachian tube function will improve.
Tinnitus, on the other hand, is not always related to hearing loss
Although tinnitus is the result of damage to the Eustachian tubes, some types of tinnitus are the result of other problems. Some people suffer from a hearing condition called inner ear infection.
If your doctor suspects that you suffer from Inner Ear Infection, you should have a test performed to determine the cause of your tinnitus. If it is Inner Ear Infection, you will need to have antibiotics and possibly surgery.
The cause of Inner Ear Infection is not yet completely known, but it is thought that it could be related to bacteria in the ear. Doctors have found that antibiotics help to clear up the infection in your Eustachian tube. This will allow you to get relief from tinnitus and ease your symptoms.
Treatment of Inner Ear Infection is similar to treating Eustachian blockage. After treatment, you will usually be able to go home and enjoy your life, without the need for prescription medication or surgery.
To prevent further damage to your Eustachian tubes, your doctor will suggest several things. They can help you avoid certain foods, avoid caffeine, and alcohol, and exercise. to help clear out toxins and eliminate the symptoms that you are experiencing. You may also be given treatments to reduce the inflammation in the Eustachian tubes.
