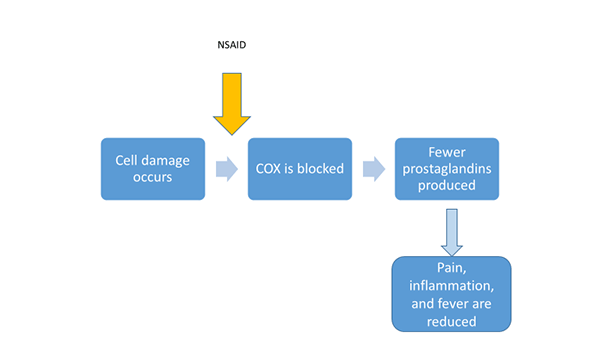
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories are common members of a group of medication class which decreases inflammation, reduces pain, prevents fluid and blood clots, lowers fevers, and in high doses, reduces the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers. The most common side effects occur due to the exact chemical structure of these anti-inflammatories, NSAIDs. Most common side effects of NSAIDs include stomach ulcers, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
NSAIDs are considered safe for most patients when taken as directed.
The possible side effects of NSAIDs are very rare
Gastrointestinal ulcers can result from stomach drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen. NSAIDs may also cause gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration and damage to the lining of the stomach and intestines. In extremely severe cases, stomach ulcers have resulted in death.
When stomach ulcers occur due to NSAIDs, the bleeding usually occurs inside the stomach and esophagus. The lining of the stomach is also damaged. In addition to this, stomach ulcers can cause severe damage to the liver, lungs and kidneys. Ulcers in the liver may lead to cirrhosis and kidney failure.
Stomach bleeding can also occur when NSAIDs are taken in combination with other medications. A patient should not take aspirin, NSAIDs or acetaminophen in combination with antacids. These medications can increase the risk of bleeding, especially when taken at night.
Ibuprofen is known to cause bleeding of the stomach, esophagus, and intestines. It can also cause gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration and damage to the lining of the stomach and intestines. If you take ibuprofen, you should avoid eating, drinking, or taking oral contraceptives or taking certain types of medications such as birth control pills if you have an existing condition such as cancer or blood clotting.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories are also known to be associated with an increased chance of heart disease, especially if they are taken over a long period of time. NSAIDs have been associated with an increased chance of stroke and increased mortality rates in people who smoke. Some studies have also indicated an increased risk of gall bladder disease in people who smoke. In addition to this, there is evidence that NSAIDs are a major cause of gastric cancer.
NSAIDs should be taken as directed for relief of pain
If you are unsure of what the proper dosage should be, speak with your doctor or pharmacist.
Before taking any medication, check with your physician or pharmacist to ensure that you are taking the safest possible side effects. NSAIDs are available in various strengths and it's very important that you do not exceed the recommended dose.
There are many reasons why stomach ulcers may occur. They include excessive intake of vitamin C, dehydration, poor diet, and improper lifestyle. If stomach ulcers occur, the most common cause is a vitamin C deficiency. Your body requires the vitamin to help regulate the production of gastric acid and prevent the growth of harmful bacteria.
If a stomach ulcer is left untreated it can lead to bleeding, ulceration and stomach surgery. It is important to treat the ulcer as soon as possible because the longer it remains untreated, the more damage will occur. Surgery may be necessary in very severe cases.
If your doctor recommends NSAIDs, be sure to use the correct dosage and to always follow your doctor's treatment. In addition to avoiding NSAIDs if you are pregnant, children, nursing mothers, or elderly people, make sure to never take aspirin or acetaminophen with other medications.
Other ways to reduce the risk of stomach bleeding or gastrointestinal bleeding is to take pain relievers such as aspirin and ibuprofen when possible. Also, avoid foods and drinks high in caffeine, alcohol, citrus fruits, coffee and other substances that may cause nausea and vomiting. If a stomach ulcer occurs, don't delay seeking medical treatment.
