Several risk factors can increase a person's risk for developing lymphoma. For example, people who are exposed to certain infections, such as Heliobacter pylori or hepatitis C, are more likely to develop NHL. Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation can also increase the risk of developing the disease. Blood tests are also important in diagnosing lymphoma. They check for the presence of certain cells and substances, as well as any signs of infection.
To diagnose lymphoma, a physical examination, blood tests, and a chest x-ray are all necessary. If the condition is detected, a biopsy will be performed. Treatment options can include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies. For instance, targeted therapy uses drugs or substances to attack cancer cells. Biologic therapy boosts the body's immune system to fight off cancer. However, people who have no symptoms may not need treatment.
Although the symptoms of lymphoma vary from person to person, there is a standard treatment for lymphoma. Patients with the disease are recommended to undergo radiotherapy and chemotherapy to alleviate the symptoms. Early diagnosis of lymphoma leads to a better outcome. Once the condition has been diagnosed, treatment options will depend on the location of the disease. It's best to see a doctor if you notice any symptoms that may be signs of the disease.
There are many different types of lymphomas. The most common type is the one that begins in the lymphatic system. This type of disease can affect anyone, including infants. It is best to seek medical help as soon as possible, as symptoms may change as the disease progresses. You may have some risk factors for developing lymphoma, but fortunately, most cases are not associated with these risk factors.
A biopsy of cancer cells in the patient's lymph nodes will reveal the cause of the cancer. A diagnosis of lymphoma is important for treatment of the disease, but it should not be delayed. In most cases, a diagnosis of lymphoma is the only way to determine the best course of treatment. Site https://truthinhealthcare.org/ will recommend suitable treatment that suits your needs. It is important to take proper precautions to prevent the disease from progressing.
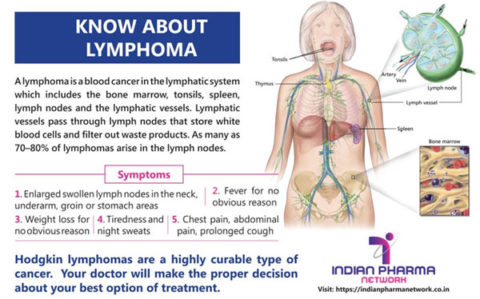
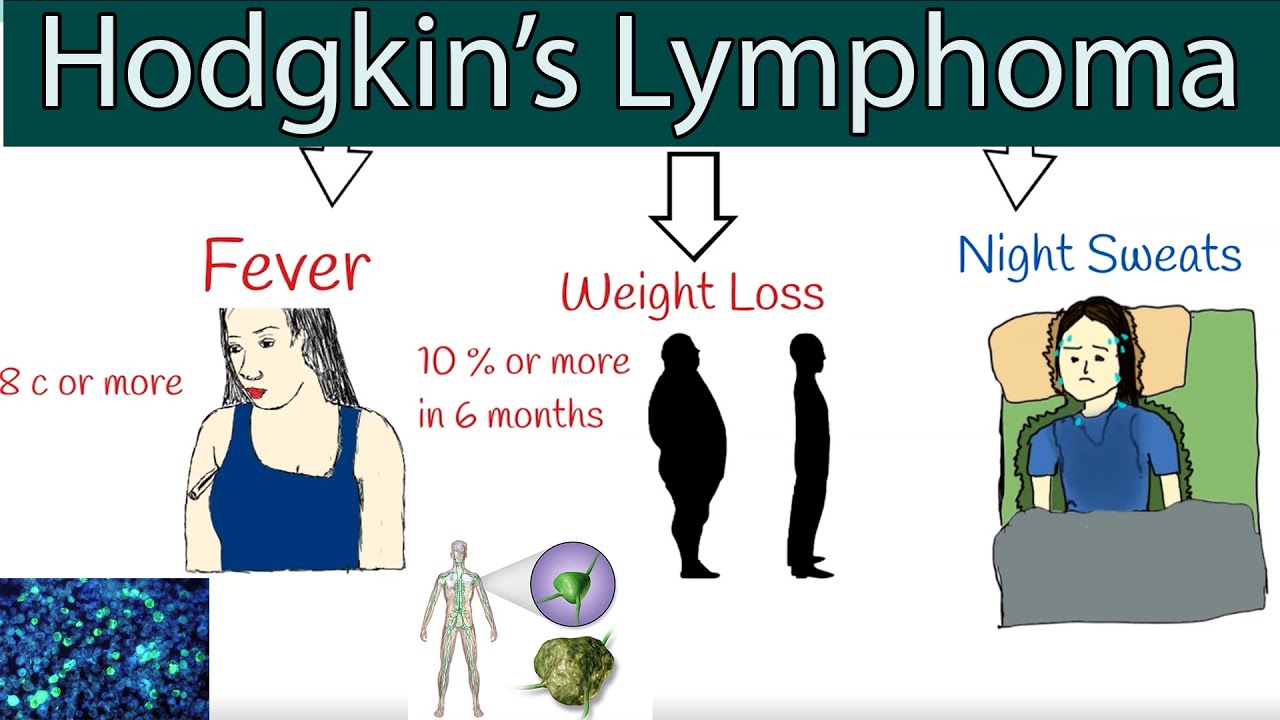
Symptoms of lymphoma include fever, swelling and pain in the lymph nodes. It can also affect the skin, liver and spleen. Despite the low incidence of lymphoma, symptoms of lymphoma should not be ignored. In fact, they can be a sign of other diseases. The doctor will ask you about your medical history and check your abdomen for inflammation. Your doctor will also look for signs of infection near the lymph nodes.
To diagnose lymphoma, a biopsy of lymph node tissue will be required. A biopsy will show whether cancer cells are related to lymphoma. Your doctor will then recommend treatment. If you have been diagnosed with lymphoma, the next step is to seek treatment. If you have any symptoms, be sure to see your doctor as soon as possible. Early diagnosis will mean a better prognosis for you.
Lymphoma is diagnosed through a physical examination and blood test. X-rays of the lymph nodes will help your doctor determine the exact type of cancer. If you have symptoms, you should see your doctor as soon as possible. It is very important to undergo a thorough diagnosis, as early diagnosis will ensure successful treatment of lymphoma. You should consult your doctor if you have any unusual symptoms.
During your lymphoma diagnosis, your doctor will perform blood tests and perform a biopsy of your lymph nodes. Once a lymphoma is diagnosed, your doctor will recommend treatment based on your specific symptoms. If your symptoms are non-existent, you may not need treatment. Nevertheless, you should be evaluated as soon as possible. In the end, the best treatment for your lymphoma is a combination of treatments suited to your individual needs.
Treatment for lymphoma is based on the stage of the disease and your overall health. If lymphoma is stage I or II, treatment will include chemotherapy and radiation. In many cases, a patient will achieve a remission following a radiotherapy treatment. In a stage III, radiotherapy may be a more suited option for the patient. This treatment will usually involve high-dose radiotherapy and chemotherapy. It will, however, have a high risk of recurrence.
